Interactive design combines user-centric layouts and dynamic content. In web design, “interactive” means pages actively respond to visitors’ actions—for example, by showing personalized content, animations, or embedded tools that users can play with. AI is transforming this field by automating creative tasks and enabling sites to adapt in real time. In fact, 62% of UX designers already use AI tools to supercharge their workflows. By combining AI-driven data insights with human creativity, small businesses and nonprofits can build websites that feel more responsive, relevant, and engaging to each visitor.
The Power of Interactive Content
Interactive web content makes users active participants rather than passive readers. Instead of static text and images, interactive elements draw users in and hold their attention. Examples include quizzes, polls, calculators, dynamic charts, chat widgets, and animated infographics. Research shows customers expect personalized interactions—over 75% will be frustrated if content isn’t relevant. By giving users choices and feedback, interactive design turns browsing into a two-way conversation. This fosters longer visits, more sharing on social media, and higher conversion rates.
Some common types of interactive contents are:
Quizzes and Assessments: Personality or knowledge quizzes that tailor results to each user’s answers (e.g., “Which product suits your lifestyle?”). These playful tools engage visitors with personalized outcomes.
Calculators and Tools: User-driven widgets (like mortgage or ROI calculators) where visitors input data and get customized results. Such tools are practical and encourage users to spend time on the page.
Personalized Recommendations: Dynamic content blocks (such as “Customers also bought...” or article suggestions) generated by AI analyzing user history. Showing tailored products or posts makes each visitor feel understood.
Chatbots and Guided Tours: AI chat windows or walkthrough guides that answer questions and direct users through features, smoothing the onboarding process. For example, a chatbot can greet first-time visitors, highlight important pages, or answer FAQs in real time.
Animated Infographics and Videos: Interactive charts or 3D visualizations that users can click, scroll, or rotate (e.g., 360° product tours or shoppable videos). Moving graphics and videos transform passive reading into active exploration.
By mixing these elements, websites feel more like engaging apps or games. AI makes it easier to create and manage such interactivity. For instance, AI prompts can quickly generate quiz ideas or even auto-build calculators from a description, optimizing the content with minimal effort.
How AI Enhances Web Design and Personalization
AI is revolutionizing how websites are built and tailored. It can analyze user data (demographics, behaviors, past purchases) to customize the site experience in real time. Major brands already do this: AI-powered recommendation engines track browsing and automatically show relevant products, boosting sales and engagement. In fact, 92% of companies are exploring AI for personalization because it can connect customers with exactly what they want.
For small businesses, this means even a simple website can behave differently for each visitor. AI might rearrange featured products, swap out images, or highlight different calls to action based on who is looking. According to the Interaction Design Foundation, AI tools enable “personalized experiences” by tailoring content and recommendations to each user. Users tend to stay on the site longer and are more likely to convert when they perceive the site as speaking to them. One concrete example: an e-commerce site might automatically generate a “shop this look” gallery based on a visitor’s style or send an email about a new product in their preferred category. These data-driven adjustments transform a generic page into a personalized, interactive experience tailored to each individual.
AI also optimizes the details of the user interface in the background. Tools like Attention Insight use AI to predict where users will look first on a page by simulating eye-tracking. This heatmap insight lets designers rearrange layouts (e.g., moving a button to a more “attention-grabbing” spot) before the site even launches, improving usability. In summary, AI in web design means dynamic personalization—the site continuously learns from each visitor and adapts the experience to keep them engaged.
AI-Powered Design Tools and Platforms
Web designers and marketers don’t have to code AI from scratch. Many modern platforms and tools embed AI features that make interactive design easier, even for non-experts. These include web builders with AI assistants and specialized UX design apps. For example:
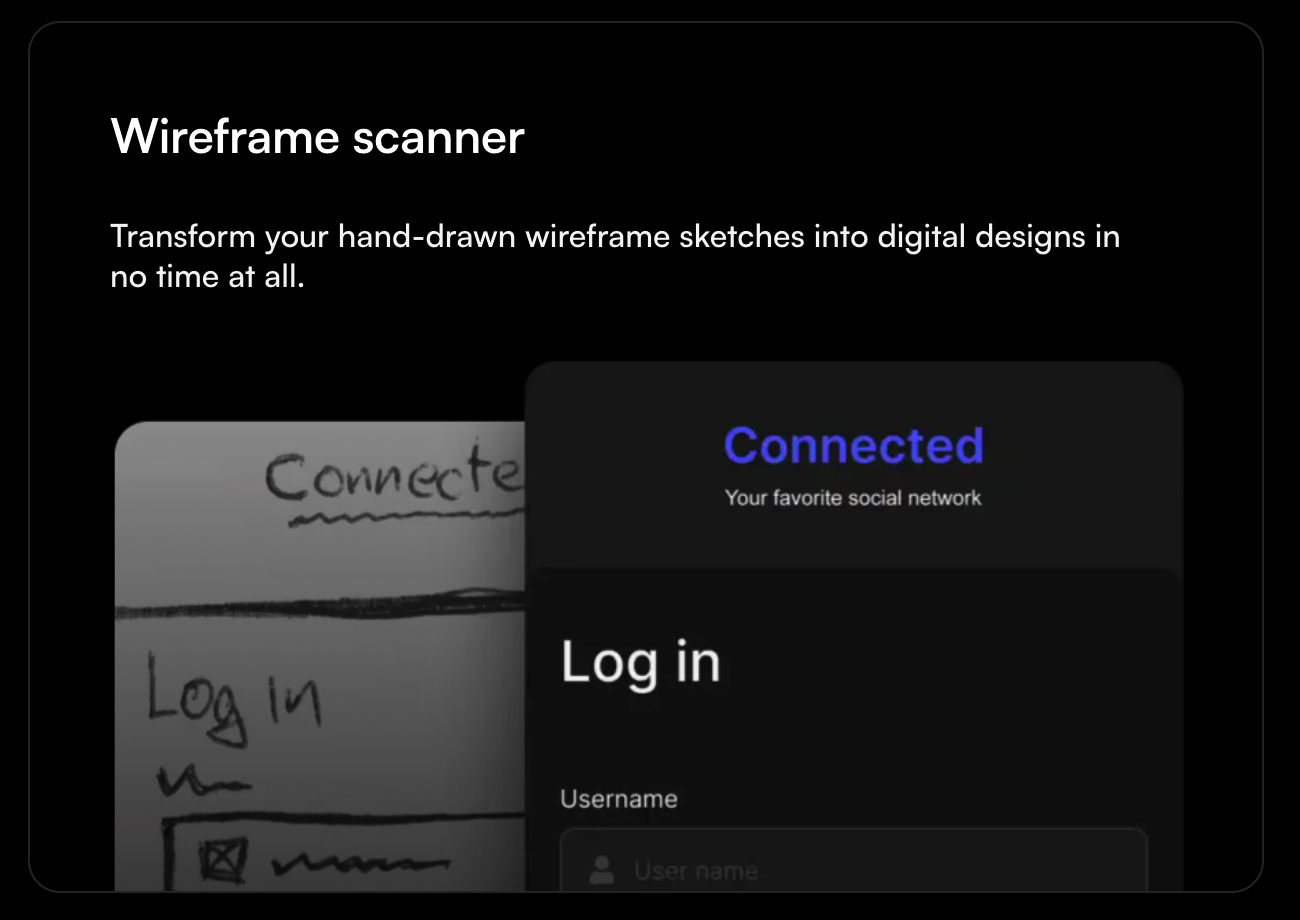
Uizard: An AI-powered wireframing tool that converts text prompts or even hand-drawn sketches into interactive UI mockups almost instantly. You might type “create a landing page with a signup form” or draw a rough layout, and Uizard generates a polished, clickable prototype without coding. This tool lets small teams quickly iterate website ideas.
Figma (with AI plugins): Figma is a collaborative design platform, and its new AI plugins (like “Magician”) can auto-generate UI layouts, icons, and text. Designers can prompt Figma’s AI to create a button, form, or entire wireframe, or ask it to write UX copy, and it delivers suggestions right in the workspace. For instance, if you need a catchy call-to-action phrase, Figma’s AI can suggest one. These smart features remove repetitive tasks so teams can focus on creative decisions.
Adobe Sensei: The AI engine inside Adobe XD, Photoshop, and Illustrator provides content-aware tools. It can automatically resize and crop images for different screens, suggest matching colors and fonts, and apply style suggestions based on context. For example, when you lay out a photo and text, Sensei might recommend a polished color palette or alignment to improve legibility. This speeds up design, ensuring even a small charity website looks professionally styled without hours of manual tweaking.
Framer AI: A generative prototyping platform that can build a live, interactive website from a simple text description. You could type “Create a one-page portfolio with a hero image and contact form,” and Framer AI generates a responsive page with animations and editable content. Designers can then refine it visually. Framer bridges design and deployment, enabling teams to prototype and even publish interactive sites without writing code.
ChatGPT (OpenAI): Though not a graphic design tool, ChatGPT excels at content ideation. As one user described it, ChatGPT functions as a creative strategist and UX copywriter at your disposal. It can brainstorm page layouts, write product descriptions, draft FAQ answers, or generate sample user personas. For example, when you ask, “Help me write 3 product page headlines,” it yields creative suggestions in seconds. His AI assistant accelerates planning and keeps content fresh, which is key for engagement.
Attention Insight: An AI analytics tool (for UX research) that predicts user attention on your mockups. It produces heatmaps that indicate where a user’s eyes are likely to focus. Designers use this feedback to adjust the placement of call-to-action elements or reduce distractions, ensuring that the page effectively guides the user.This kind of AI validation means you catch issues early, before coding or launching.
Content and Imaging AI: Beyond layouts, AI tools can create the actual content and visuals. Platforms like Adobe Firefly or DALL·E let you generate custom images and illustrations from a text prompt (e.g., “an abstract background for a tech blog”). These images can be embedded or animated on your site. Interactive content tools (e.g., Outgrow, Copy.ai) use AI to help craft quizzes, calculators, and polls—from generating questions to designing the user flow. Even email subject lines and calls to action can be A/B tested and optimized by AI to get more clicks.
Overall, these AI-enabled platforms let even lean teams build sophisticated web experiences. They handle the grunt work (layout resizing, image editing, copywriting suggestions), which frees designers and marketers to focus on strategy. The result is faster turnaround and more polished interfaces.
Practical Benefits and Future Outlook
For startups, small businesses, and charities—AI-driven interactive design has clear perks:
Increased Engagement: Interactive elements catch and hold visitor attention better than static pages. AI makes personalization easy (dynamic content, chat assistance, personalized emails), leading to higher click-through and conversion rates.
Cost and Time Savings: Many routine tasks become automated. A small team doesn’t need to hand-code every layout or write all copy from scratch. AI tools can generate first drafts of page text, images, or layouts, slashing development time. This lets businesses launch or update websites faster.
Data-Driven Insights: AI can gather and analyze user interactions (through chat logs or click heatmaps) and suggest iterative improvements. For example, if an AI chatbot logs common queries, the site can add quick links to those answers. Attention Insight’s heatmaps let you refine design based on predicted eye movement. Over time, the website evolves to better match user needs.
Accessibility: AI can improve accessibility too—automatically adding alt-text to images, optimizing contrast, or even translating content into other languages to reach a broader audience. (Some AI tools detect if a site is hard to navigate and suggest fixes.) This means more inclusive experiences out-of-the-box.
Looking ahead, interactive design with AI will only grow more sophisticated. Emerging trends include voice assistants on websites (AI that listens and answers queries via speech) and AR/VR experiences (virtual showrooms or try-ons powered by AI). Even today, brands are experimenting: for instance, using AI to create chat-driven shopping or to tailor entire page layouts on the fly as soon as the user lands. But one key point remains: AI won’t replace human creativity. As one design expert advises, the future of UX is “AI + expert human judgment.” In other words, AI should handle repetitive tasks and personalization logic, while people focus on brand story, empathy, and originality.
In conclusion, AI-powered interactive design offers an exciting path for small businesses to boost their online presence. By leveraging AI tools—from chatbots and personalization engines to design assistants and generative content platforms—even non-technical teams can create websites that feel dynamic and engaging. The technology is rapidly maturing: today’s AI helps build the site; tomorrow’s will learn and adapt it. For any organization wanting to stand out online, investing in AI-driven interactivity can pay off in more user engagement, better customer satisfaction, and ultimately higher ROI.